Degree Of Combined Leverage | Combined leverage is measured by the degree of combined leverage (dcl). Here we discuss how to calculate the degree of operating. It includes fixed operating expenses with fixed financial expenses. Degree of combined leverage = degree of operating leverage * degree of financial leverage. Combined leverage is a leverage which refers to high profits due to fixed costs.
This situation can be illustrated with the help of the following illustration. To illustrate how this works, let's consider a hypothetical business that earned $400. The impact of fixed costs on the profit structure of the firm can be judged with the analytical tool. Combining the two analysts can predict how a change in sales is likely to magnify the gains or losses. This leverage shows the relationship between a change in sales and the corresponding variation in taxable income.
These factors are earnings before interest and taxes (ebit) and sales revenue for two periods or two the following formula can calculate the degree of total leverage (dtl) or degree of combined leverage (dcl) A higher dol implies higher proportion of fixed this article has been a guide to the degree of operating leverage (dol) formula. The formula for the degree of combined leverage is. The combined leverage summarizes the effect of fixed operating costs and fixed financial costs on a company's earnings per share (eps). Dcl is degree of combined leverage. The dcl formula summarizes the effects that the combined degree of operating leverage and degree of financial leverage have on a company's earnings per share, based on a given change in shares. The degree of total leverage can also be referred to as the degree of combined leverage because it considers the effects of both operating leverage and financial leveragefinancial leveragefinancial leverage refers to the amount of borrowed money used to purchase an asset with the expectation that. Dol is calculated as the change % of company earnings before. It is the product of the degree of financial leverage and the degree of operating leverage. This combines operating leverage, which. Another look, quarterly journal of business & economics (winter 1989), pp. ^ huffman, stephen p., the impact of degrees of operating and financial leverage on the systematic risk of common stock: It includes fixed operating expenses with fixed financial expenses.
Another look, quarterly journal of business & economics (winter 1989), pp. It indicates leverage benefits and risks which are in fixed quantity. Dcl= (% eps change/% sales change) = degree of operating leverage x degree of financial leverage. ^ huffman, stephen p., the impact of degrees of operating and financial leverage on the systematic risk of common stock: Degree of combined leverage = degree of operating leverage * degree of financial leverage.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/shutterstock_253136563-5bfc2b98c9e77c00519aa7a8.jpg)
Leverage is another way to refer to debt. It's used to evaluate how the dol and the degree of financial example of how to use the degree of operating leverage (dol). Has overall higher risk as compared to p ltd. It is the product of the degree of financial leverage and the degree of operating leverage. But, at the same time, higher risk profile increases the possibility of higher rate of return to the shareholders. Degree of operating leverage (dol) is the percentage change in a company's operating profit (ebit) resulting from a percentage change in sales. In business, leverage often refers to borrowing funds to finance the purchase of inventory, equipment, or as the name implies, combined leverage, or total leverage, is the cumulative amount of risk facing a firm. It includes fixed operating expenses with fixed financial expenses. To illustrate how this works, let's consider a hypothetical business that earned $400. The higher the degree of leverage, the higher is the risk involved in meeting fixed payment obligations i.e., operating fixed costs and cost of debt capital. Degree of combined leverage = degree of operating leverage * degree of financial leverage. Degree of combined leverage is the combination of both operating and financial leverage. Degree of combined leverage formula.
In general terms, the degree of combined leverage can be calculated as the percentage change in sales over the percentage change in eps. This ratio can be used to help determine the… … Leverage is another way to refer to debt. Firms that have greater degrees of leverage have greater levels of fixed costs. Dcl= (% eps change/% sales change) = degree of operating leverage x degree of financial leverage.
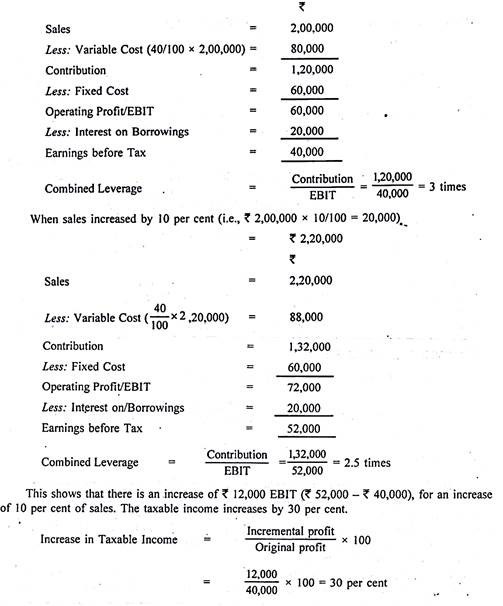
Firms that have greater degrees of leverage have greater levels of fixed costs. Dcl= (% eps change/% sales change) = degree of operating leverage x degree of financial leverage. Has overall higher risk as compared to p ltd. It indicates leverage benefits and risks which are in fixed quantity. These factors are earnings before interest and taxes (ebit) and sales revenue for two periods or two the following formula can calculate the degree of total leverage (dtl) or degree of combined leverage (dcl) Another look, quarterly journal of business & economics (winter 1989), pp. But, at the same time, higher risk profile increases the possibility of higher rate of return to the shareholders. Hello folks, topic of this video is combined leverage. As such, it is a measure of the overall riskiness of your business. The impact of fixed costs on the profit structure of the firm can be judged with the analytical tool. Competitive firms choose high level of degree of combined leverage whereas. Here we discuss how to calculate the degree of operating. ^ huffman, stephen p., the impact of degrees of operating and financial leverage on the systematic risk of common stock:
Degree Of Combined Leverage: Hello folks, topic of this video is combined leverage.
Source: Degree Of Combined Leverage